The dream of being able to automatically translate from one language to another has come true. But just how effective is machine translation? What are the requirements for adopting Neural Machine Translation?
In this post, we aim to de-mystify machine translation by providing you with the information you need to decide whether machine translation is the translation technology solution you are looking for.
What is machine translation and how does it work?
Let’s start with some basic definitions. Machine translation is the process done by a computer to convert text from one language to another using one or a combination of the following methods:
Rule-based machine translation (RBMT) – Uses language and grammar rules combined with specific dictionaries to generate translations.- Statistical machine translation (SMT) – Generates translations using statistical models created from the analysis of large databases of multilingual content (bilingual text corpora)
- Neural machine translation (NMT) – Today’s dominant method, NMT uses deep learning based on artificial neural networks to provide faster and more accurate translations.
How accurate is neural machine translation?
The quality of machine translation output will depend on various factors:
- the configuration of the machine translation engine
- the quality of the source text
- the domain of the source text
- the language combination
- the amount of previously translated material available for training
Even when the above factors are optimized, there is no guarantee that the machine translation output will be free of errors, even potentially significant errors.
Machine translation on its own – usually called raw or pure MT - is therefore used only for specific use-cases. There must be an agreed-upon tolerance level of potential mistranslations and other errors in the MT output.
When the tolerance level for errors is understood, raw machine translation can be a powerful tool to solve translation challenges like limited budgets or big volumes that must be translated quickly.
For the use-cases when potential errors in the machine translation are not acceptable, the language service industry uses integrated processes that combine MT with human post-editing of the machine translated text.
How does neural machine translation post-editing work?
Post-editing consists of carrying out an in-depth proofread of a text that has been translated by a machine translation engine. If available, the glossary and translation memories are also part of the process, and the post-editor is responsible for ensuring approved terminology is applied.
The post-editing process is different from the revision process. A revision is a secondary review (quality assurance) of a translation that is assumed to already follow all specifications and instruction and be of high quality.
Post-editing, on the other hand, is more like the initial translation, except that the post-editor has the benefit of the machine translation to work with to increase his or her productivity. During the post-editing process, just like they would during a translation from scratch, the post-editors ensure that the company tone, terminology and other linguistic requirements are followed.
It is important for a post-editor to have the right skill set to work with machine translated content. Our post-editors undergo training, and we follow the ISO 18587:2017 standard for post-editing.
How does neural machine translation work with Computer Assisted Translation (CAT) tools?
Machine translation is integrated into the translation process in the CAT tool. Results from the Translation Memory have priority and will be proposed to the translator when available. The machine translation engine is used to pre-translate new content that does not have previously translated Translation Memory matches.
Below, you can see a general neural machine translation project workflow:
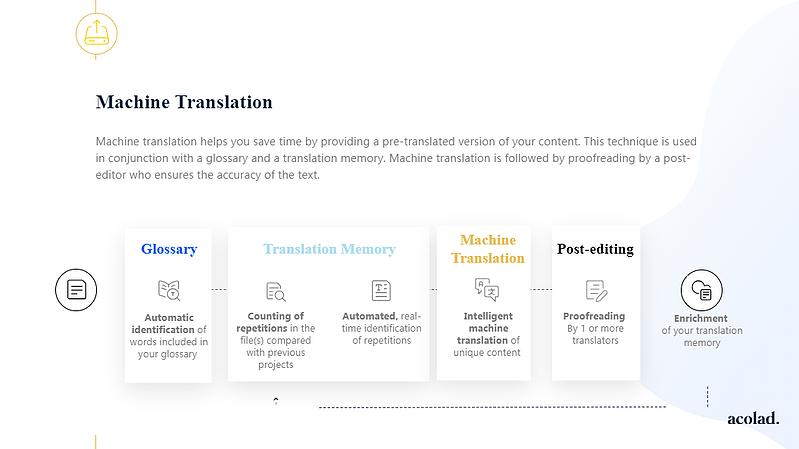
What is neural machine translation used for?
When it comes to offering machine translation with post-editing to our customers, we generally propose the following service levels for the different MT use cases:
Raw Neural Machine Translation: machine translated text is delivered as is without any human intervention. We recommend that you only use this option when you need to obtain the overall gist of a text. It is the least expensive alternative as it requires less initial set up and resources.
Neural Machine Translation with Post-editing: This option is ideal for content that needs to be published or widely distributed. Human translators perform complete corrections of the machine translation output to make sure that it is adapted to the target audience, the tone and style are appropriate, and it matches the content’s messages in the source language.
What are the requirements for adopting neural machine translation?
For a long time, adopting an integrated machine translation process only made sense for certain types of content and for limited language pairs. However, continuous technological improvements now allow us to better translate more language pairs and all type of contents in terms of output quality. An analysis of content types and translation needs can provide valuable insight into where machine translation can have the most impact in the translation process.
How much can you save with neural machine translation?
Contrary to what many people think, using machine translation will not completely reduce your translation budget (unless you just concentrate on using raw machine output for gisting purposes), but depending on your specific situation, you may be able to save up to 50% on translation costs.
Are you ready to take the next step?
If you think that your translation processes can be further optimized with machine translation solutions, contact us for a free consultation. Our experts will be able to advise you on the suitability of your content and provide the best technology recommendation for your content translation workflows.
Unveiling the meaning of machine translation quality
Understand the different approaches to evaluate machine translation quality and what they mean for your translation and localization needs.

